
Chennai
As these clinics are easily accessible and are available in large numbers, patients tend to flock to these centres, irrespective of whether they have the basic facilities required for the procedures or not.
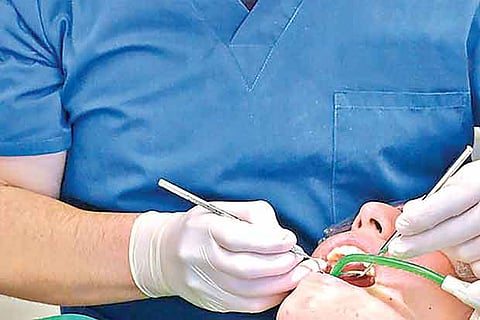
Stating that with the development in technology, dental procedures like a root canal treatment have been made much simpler, Dr Yashwanth Venkataraman, Medical Director, Parasu Dental Centre, said, “Earlier, it would be a three-visit procedure - each visit extending to half an hour. However, now, it can be completed in one sitting. Nowadays, we have machines to monitor the root canal to suit the convenience of the patient and the doctor and because of this advancement in technology, we can complete one root canal in about 15 to 20 minutes, unless it is infected.”
However, while the procedures are being made simpler, the need for basic equipment and facilities at the clinics is essential, for which no inspection is done due to the lack of a body to monitor it - unless a complaint is made by a patient or a doctor. “There have been a number of cases brought to light of negligence on the part of some of these dental clinics. However, no written complaints have been made. How then is one supposed to feel safe when approaching a clinic for treatment?” opined a medicare activist.
“While it is considered alright for a patient to be administered sedation – in the case of a painful procedure or if the patient is very sensitive and cannot undergo a root canal under local anaesthesia – it is important that only an anaesthetist administers it,” said an anaesthetist from a recognised hospital in the city. He added that it is also advisable that the patient be allowed to rest, once out of sedation.
Stressing on the need for an evaluation to be done prior to the procedure, Dr George Thomas, former editor, Indian Journal of Medical Ethics, said, “The line between sedation and anaesthesia is thin. However, the aim is to give sufficient pain relief to the patient to complete the procedure successfully. It is important for a clinic or hospital to have the basic facilities to undertake a procedure on a patient who may have had other illnesses. Therefore, there should be a body to ensure that each clinic has sufficient infrastructure to handle every case that is brought to them.”
However, due to the lack of a set protocol, it has been seen that not all dentists follow the same etiquette. In the case of sedation, there exists no set guideline in India, nor is there a specific course wherein anybody can get trained in sedation. Only an anaesthetist or a dentist who has got a certification abroad can perform sedation. “Sedation in India is being used only recently – for the past 15 years or so. Generally, a patient is advised sedation only for painful procedures. In the case of a root canal, unless the patient is very sensitive, it is not advised. As the patient is drowsy once out of sedation, it is best not to perform any further procedures,” he added.
With the availability of a ‘scale’ under the American Society of Anaesthesia which tells the pre-operative risk of the patient – grading the risk from one to four — experts say that it must be followed. “If a patient is evaluated, sufficient precautions can be taken to ensure that whatever condition he may have can be handled in the centre. As monitoring has become much better over the years, the occurrence of negligence is unacceptable,” said a Health expert.
Stating that the Dental Council of Tamil Nadu, which has to play the role of evaluating the capacity of the dental clinics to handle such issues, is not doing so, Dr Yashwant said, “The council has now become only a registering body. It must be a body that also evaluates the clinics’ capacity to handle medical emergencies — whether the clinic is functioning with normal protocol or not. The council has the authority to make a rule but unfortunately, they do not do it. However, no one has questioned them as such a problem has never risen.”
On its role of preventing such cases, a Health department official, speaking on condition of anonymity, said, “The Council is only the state chapter of the Dental Council of India, and it is a statutory body, recognised by the Government of Tamil Nadu and the Dental Council of India. While it does not conduct any inspections, if there is any complaint made by an individual or any doctor, then an enquiry is conducted.”
Stating that the government is coming up with a Clinical Establishment Act, he said, “Most probably once it comes and is implemented, based on the government instructions, checks will be made.”
Procedures in place
Protocols to be followed in performing a root canal under sedation
Understanding the anatomy of a tooth
Endodontic treatment treats the inside of the tooth. Root canal treatment is one type of endodontic treatment. To understand endodontic treatment, it helps to know something about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is a soft tissue called the pulp. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves and connective tissue and creates the surrounding hard tissues of the tooth during development. The pulp extends from the crown of the tooth to the tip of the roots where it connects to the tissues surrounding the root. The pulp is important during a tooth’s growth and development. However, once a tooth is fully mature it can survive without the pulp, because the tooth continues to be nourished by the tissues surrounding it.
Endodontic treatment can often be performed in one or two visits and involves the following steps:
The endodontist examines and x-rays the tooth, then administers local anesthetic. After the tooth is numb, the endodontist places a small protective sheet called a “dental dam” over the area to isolate the tooth and keep it clean and free of saliva during the procedure.
The endodontist makes an opening in the crown of the tooth. Very small instruments are used to clean the pulp from the pulp chamber and root canals and to shape the space for filling.
After space is cleaned and shaped, the endodontist fills the root canals with a biocompatible material, usually a rubber-like material called gutta-percha. The gutta-percha is placed with an adhesive cement to ensure complete sealing of the root canals. In most cases, a temporary filling is placed to close the opening. The temporary filling will be removed by your dentist before the tooth is restored.
After the final visit with your endodontist, you must return to your dentist to have a crown or other restoration placed on the tooth to protect and restore it to full function. If the tooth lacks sufficient structure to hold the restoration in place, your dentist or endodontist may place a post inside the tooth. Ask your dentist or endodontist for more details about the specific restoration planned for your tooth.
— Source: American Association of Endodontists
Visit news.dtnext.in to explore our interactive epaper!
Download the DT Next app for more exciting features!
Click here for iOS
Click here for Android